DEFINITION
It is considered TIA (transient ischemic attack) focal neurological event of vascular etiology and symptoms lasting less than 24 hours. By definition leaves no visible damage to the brain imaging test (preferred by the RM should consider sensitivity without injury after the episode).
This classic definition has tried in recent years to be modified since the vast majority of transient ischemic events last for a few hours. 60% less than 1 hour and almost 90% less than 6 hours. Unlike the events lasting more than 6 hours and less than 24 hours if we make a very high percentage MRI acute injury therefore it would not be a show AIT.
The importance of a TIA is that more than 10% of cases will develop in the next month a stroke.
CLINIC
The clinical presentation of AIT can be divided into 3 types: amaurosis fugax, hemispherical and trunk.
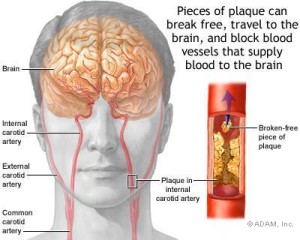
-The Amaurosis fugax is loss of transient monocular vision vascular involvement central retina artery due to a plunger or poor perfusion by stenosis / carotid occlusion.
-The hemispheric TIA, motor, hemifield visual, sensory or language intracranial vessel occlusion or poor perfusion occlusion / carotid stenosis deficit.
-The brainstem AIT is similar to the above but accompanied by instability, limb loss or impairment of cranial nerves that guides vascular involvement vessels supplying the brain stem.
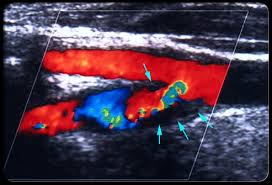
The division into these three groups lies in the prognosis and risk of a new TIA a stroke . Amaurosis fugax represents the lowest risk of future stroke therefore followed by the hemispheric and brainstem AIT at high risk of new vascular event, and which requires a urgent vascular study (ECOTSA, or transcranial Doppler study Angio-MR or CT) ( Less 24-48h).
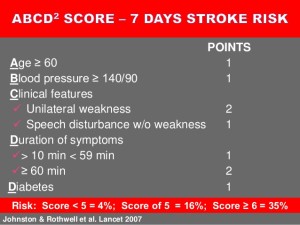
They have tried to define scales AIT according to clinical parameters to predict the risk of the emergence of new stroke or a new AIT. One ABCD2 the best known, although it seems something is not sensitive and specific enough in our country despite the publication of more than five years on it.
DIAGNOSIS
Only urgent assessment study and a specialist in neurology hospital with 24h that allows for CT, ECG, chest X-ray urgently and most importantly, a vascular study with carotid ultraosund +/- transcranial Doppler rule allowing a treatable vascular involvement is a secondary prevention guarantee that far exceeds the application of scales.
Only cases of very remote places in our country for evaluation that requires a large displacement and not have that structure may be differentiated (no great evidence but common sense) two subgroups: high-end and high risk. In the first group would focus which there murmurs in supra-aortic trunks, or arrhythmia or frequent premature beats in ECG or hemispheric TIA clinic or trunk or several episodes of AIT and entail imminent referral to a tertiary hospital in the first means of transportation available. The second group after a careful observation should be referred for assessment preferent-urgent but always within the first 24h-48h.
TREATMENT
Secondary prevention treatments did not differ from those of a stroke. If confirmed by a specialist AIT antiplatelet therapy with aspirin in doses of 100 or 300 mg / day is ideal because of its quick action, the amount of lipid-lowering drugs (statins, pej atorvastatin 20 mg or 40 mg / day) in case of suspected etiology atherothrombotic may be effective and beneficial in acute phase although no clear evidence is available in this regard.
If TIA is associated to cardioembolic source (atrial fibrilation) and there are no contraindications patients must be anticoagulated in stead antiagregation. Low molecular weight heparin or sodium heparin are those with immediate anticoagulant effect and ideal for the secondary prevention of cardioembolic TIA .
However the appearance of new oral anticoagulants or direct action are positioned as one of the most effective treatments to classic anticoagulants and its fast action in these situations as the AIT. Both dabigratran as apixaban and rivaroxaban can be some good and effective treatments provided there are no contraindications and etiology of AIT is a non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
It is very important to confirm that diagnosis of TIA by CT or MRI brain hemorrhage and discard or other process before starting antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy. We have to confirm the ischemic nature of cataloged as AIT process.
At the same time it is important not drop either treat high blood pressure below 185/110 in the first 24 hours. If you do not have a full study (ECOTSA-DOPPLER) that discard severe carotid or vertebrobasilar stenosis or occlusion, you must not decrease blood pressure bellow this target.